The tenth way of improving quality is continual improvement.
Continual improvement is when the improvement is step by step. It is one of the constant and surest ways of improvement. The organization has to continually improve its Quality Management System in the aspects of its effectiveness, suitability and adequacy. Continual improvement has to be a recurring activity to enhance the performance of its QMS.
Another way of improving quality as per ISO 9001:2015 standard is breakthrough change.
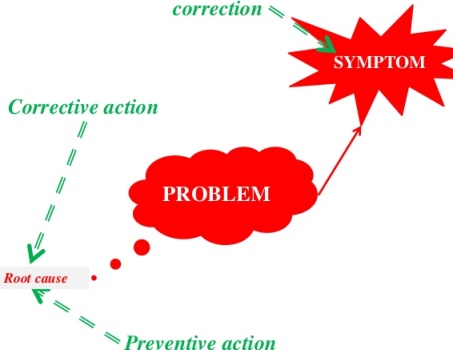
By breakthrough, it is meant that a significant change in the performance of the process is a result of determined human effort and not luck. A chance change in the system can also result in the improvement of the processes, but if we do not understand what exactly the change is, it is possible that the performance may deteriorate. Thus, the processes must be studied and a theory for improvement has to be proposed, tested, verified and then implemented. Only then the breakthrough will occur.
Breakthrough change is one of the examples of improvement mentioned in clause number 10.1. Quality improvement has often happened in the history of mankind by invention or breakthrough change.
Eurotech, an IRCA approved training partner (ATP), is conducting ISO 9001:2015 trainings in your city. To know more about this training, drop an email at trg@eurotechworld.net or call us at +91 9316744482 or 0172 - 4191128.